

A Unicast MAC address frame is only sent out to the interface which is assigned to a specific NIC and hence transmitted to the single destination device. The Unicast MAC address represents the specific NIC on the network. There are three types of MAC addresses, which are: The MAC address can be represented in below three formats:.Vendors or manufacturers can use any sequence of digits to the NIC specific digits, but the prefix should be the same as provided by the IEEE. The last three octets are NIC specific and used by the manufacturer to each NIC card.Some example of OUI of known vendors are:.
ANDROID MAC ADDRESS CLONE REGISTRATION
These MAC prefixes are assigned to each organization or vendor by the IEEE Registration Authority Committee.
The first three octets are used as the OUI or Organisationally Unique Identifier. It is divided into six octets, and each octet contains 8 bits. It is 12 digits or 6-byte hexadecimal number, which is represented in colon-hexadecimal notation format. So, let's understand how it is configured and what format is selected. We can understand this example with the below image: Format of MAC addressĪs we have already discussed in the above section, we cannot assign the MAC address to the device's NIC it is preconfigured by the manufacturers. If device A sends a data frame to the address 00000ABB28FC, the switch will fail to deliver this frame to the destination, as it has two recipients of this data frame. The NIC of devices B and C have the same MAC address. The MAC addresses of these devices are 11000ABB28FC, 00000ABB28FC, and 00000ABB28FC, respectively. Suppose three devices A, B, and C are connected to a network through a switch. If a LAN network has two or more devices with the same MAC address, that network will not work. Why should the MAC address be unique in the LAN network? We have the IP address to identify the device through different networks, we still need a MAC address to find the devices on the same network. On the other hand, the IP addresses are used on layer 3 and help identify the devices on different networks. 
The MAC address works on layer 2 and helps identify the devices within the same broadcast network (such as the router). When we request a page to load on the internet, the request is responded and sent to our IP address.īoth MAC and IP addresses are operated on different layers of the internet protocol suite. The answer to this question is that every mac address is assigned to the NIC of a hardware device that helps to identify a device over a network. Reason to have both IP and MAC addresses.Īs we already had the IP address to communicate a computer to the internet, why we need the MAC address.
The ARP protocol is used to associate a logical address with a physical or MAC address. It is provided by the device's vendor at the time of manufacturing and embedded in its NIC, which is ideally cannot be changed. It works on the data link layer of the OSI model. It is 12-digit, and 48 bits long, out of which the first 24 bits are used for OUI(Organization Unique Identifier), and 24 bits are for NIC/vendor-specific. It is represented in a hexadecimal format on each device, such as 00:0a:95:9d:67:16. It is globally unique it means two devices cannot have the same MAC address. It stands for Media Access Control, and also known as Physical address, hardware address, or BIA (Burned In Address). It is assigned to the NIC (Network Interface card) of each device that can be connected to the internet. To make communication between two networked devices, we need two addresses: IP address and MAC address. 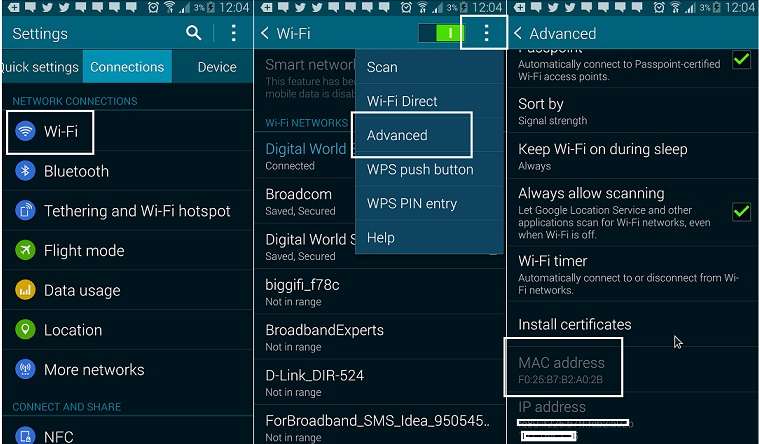
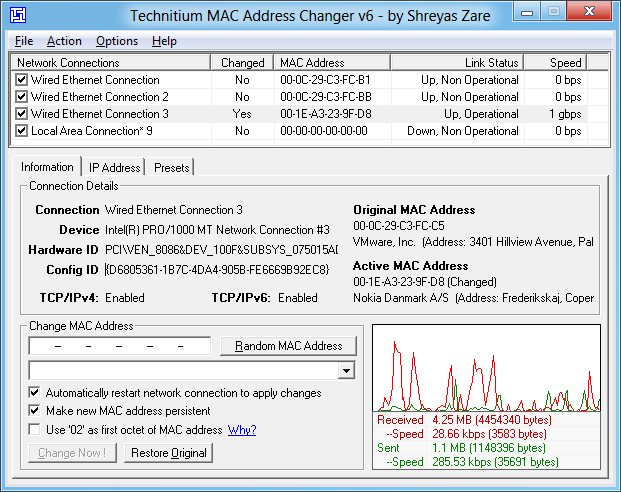
MAC address is the physical address, which uniquely identifies each device on a given network.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
